The medical landscape has witnessed significant advancements over the years, particularly in the management of chronic diseases like diabetes and obesity. One of the most promising developments in recent times is the use of GLP-1 receptor agonists. These medications have transformed the approach to treating type 2 diabetes and obesity. By offering a new pathway to improved health outcomes. This blog will explore the role of GLP-1 receptor agonists in modern medicine. And focusing on their benefits, types, side effects, and ongoing research.
What Are GLP-1 Receptor Agonists?
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, also known as GLP mimetics, function similarly to the natural hormone GLP-1 in the body. GLP-1 is an incretin hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating glucose metabolism by enhancing insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release, and slowing gastric emptying. These effects contribute to improved control blood sugar , helping people with diabetes effectively manage their health condition.
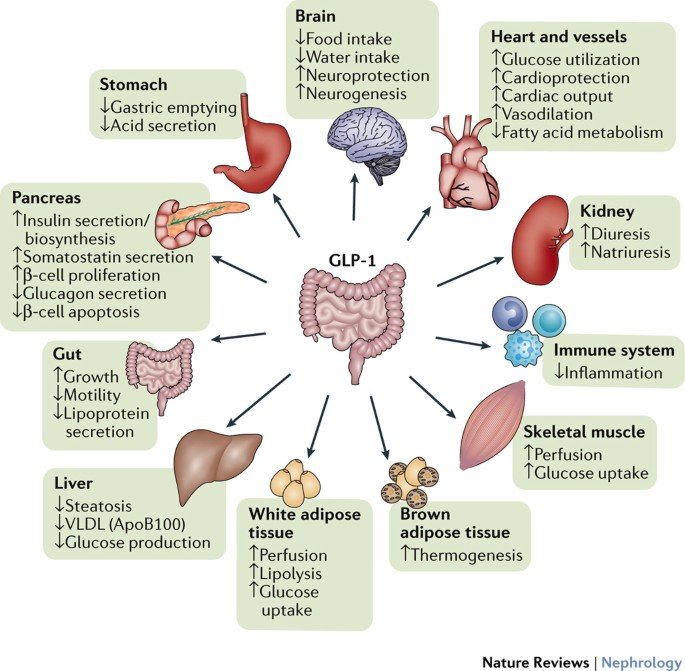
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Diabetes Management
Enhancing Insulin Production
One of the primary mechanisms by which GLP-1 receptor agonists assist in managing diabetes is by enhancing insulin production. When blood sugar levels rise, GLP receptor agonists stimulate the pancreas to release insulin, helping to lower blood glucose levels. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes, who often have diminished insulin production. Managing blood sugar effectively is critical, as high blood sugar levels can lead to various complications, including an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and high cholesterol levels.
Reducing Glucagon Secretion
In addition to boosting insulin secretion, GLP-1 receptor agonists also reduce the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood glucose levels by signaling the liver to produce and release glucose into the bloodstream. By lowering glucagon levels, GLP-1 receptor agonists help further manage your blood sugar, making them a vital component of modern diabetes management.
Types of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Several GLP-1 receptor agonists are currently available, each with unique characteristics that may make them suitable for different patient needs. Some of the most commonly prescribed GLP receptor agonists include:
- Exenatide (Byetta, Bydureon): Approved as one of the early GLP receptor agonists, exenatide is injected and recognized for its capacity to decrease blood sugar levels and encourage weight loss.
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity): Dulaglutide is a once-weekly injection that offers convenience for patients who prefer less frequent dosing.
- Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy): Available as both a once-weekly injection and an oral tablet, semaglutide is recognized for its potent effects on blood sugar control and weight loss, making it particularly beneficial for people with diabetes who also struggle with obesity.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Weight Loss
GLP-1 Weight Loss Benefits
Beyond their role in diabetes management, GLP receptor agonists have gained attention for their significant weight loss benefits. Studies have shown that these medications can help individuals lose a substantial amount of weight, particularly when combined with lifestyle interventions like diet and strength training.
With approval as one of the earliest GLP-1 receptor agonists, exenatide is injected and acclaimed for its effectiveness in reducing blood sugar levels and aiding in weight loss. This makes them a valuable tool in the treatment of obesity, a condition that is common in people with diabetes and increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and related health complications.
Obesity Treatment with GLP-1 Agonists
GLP receptor agonists like liraglutide (Saxenda) and semaglutide (Wegovy) have been specifically approved for the treatment of obesity. These medications have been shown to produce weight loss of up to 15% of body weight, offering new hope for individuals struggling with obesity-related health issues such as heart disease, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
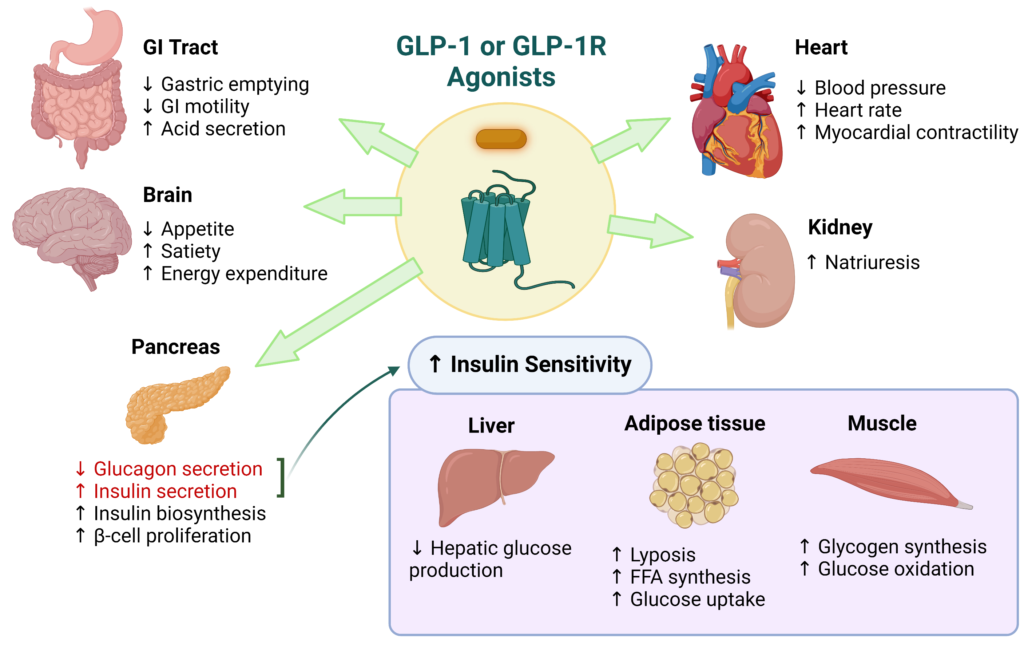
Side Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
As with any medication, GLP-1 receptor agonists are associated with potential side effects. The most common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These side effects are usually mild and tend to diminish over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
In rare cases, GLP receptor agonists have been associated with more serious side effects, such as pancreatitis and gallbladder disease. Therefore, it is essential for patients to discuss their medical history with their healthcare provider before starting a GLP receptor agonist. This is particularly important for individuals with a history of gallbladder issues or those who have undergone gallbladder removal, as these conditions could potentially be exacerbated by GLP medications.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists vs. Semaglutide
Semaglutide, a type of GLP-1 receptor agonist, has garnered significant attention for its efficacy in both diabetes management and weight loss. But how does it compare to other GLP receptor agonists?
Semaglutide is often considered more potent than other GLP-1 receptor agonists, with clinical trials showing greater reductions in blood sugar levels and more substantial weight loss. Its availability in both injectable and oral forms also adds to its appeal, offering flexibility for patients. However, semaglutide may also be associated with a higher incidence of gastrointestinal side effects, making it essential for patients and healthcare providers to weigh the benefits and risks when choosing a GLP-1 receptor agonist.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
The role of GLP-1 receptor agonists in modern medicine is continuously evolving, with ongoing research exploring their potential applications beyond diabetes and obesity management. Some areas of interest include:
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Research has shown that GLP receptor agonists may have protective effects on the heart, reducing the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational Diabetes: Emerging studies suggest that GLP-1 receptor agonists may offer benefits in managing gestational diabetes. Which is a health condition that increases the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Emerging studies suggest that GLP receptor agonists may have neuroprotective properties. Which potentially offers benefits in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease.
- Liver Health: There is growing interest in the potential role of GLP receptor in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Which is a condition closely linked to obesity and type 2 diabetes.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Modern Diabetes Management
The introduction of GLP-1 receptor agonists has revolutionized the approach to managing type 2 diabetes. These medications offer a multifaceted approach to blood sugar control, addressing multiple pathways involved in glucose regulation. Their ability to enhance insulin production, reduce glucagon secretion, and promote weight loss makes them a cornerstone of modern diabetes treatment.
Furthermore, GLP receptor agonists offer advantages over other diabetes medications, such as sulfonylureas and insulin. By reducing the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and promoting weight loss rather than weight gain. This makes them particularly attractive for individuals with type 2 diabetes who are also overweight or obese.
The Future of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
As research continues, the potential applications of GLP-1 receptor agonists in medicine are likely to expand. The investigation into the role of cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and liver diseases in treatment is an ongoing process. Future studies may reveal even more benefits of these versatile medications.
For individuals struggling with type 2 diabetes, obesity, or other related health conditions, GLP-1 receptor agonists offer a promising treatment option that can lead to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life. As our understanding of these medications grows, their impact on modern medicine will likely continue to increase.
Conclusion
GLP receptor have emerged as a powerful tool in modern medicine, offering significant benefits in managing type 2 diabetes and obesity. Their ability to improve blood sugar control, promote weight loss, and potentially offer additional health benefits makes them a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal. With ongoing research revealing new applications, GLP receptor agonists are on track to become a crucial component in healthcare, tackling some of the most pressing health challenges.
Don’t wait any longer—contact us today to schedule your consultation. And also discover how Semaglutide can help you achieve your weight loss goals. Feel Free to reach us at 312-312-7873.
